Professional Diploma in Sports Nutrition - Module 1 Lesson 2
Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates as fuels for exercise
- Stored as glycogen in liver and muscles
- Maintain blood glucose levels
Men
- Liver Glycogen - 90g
- Muscle Glycogen - 400g
Women
- Liver Glycogen - 70g
- Muscle Glycogen - 300g
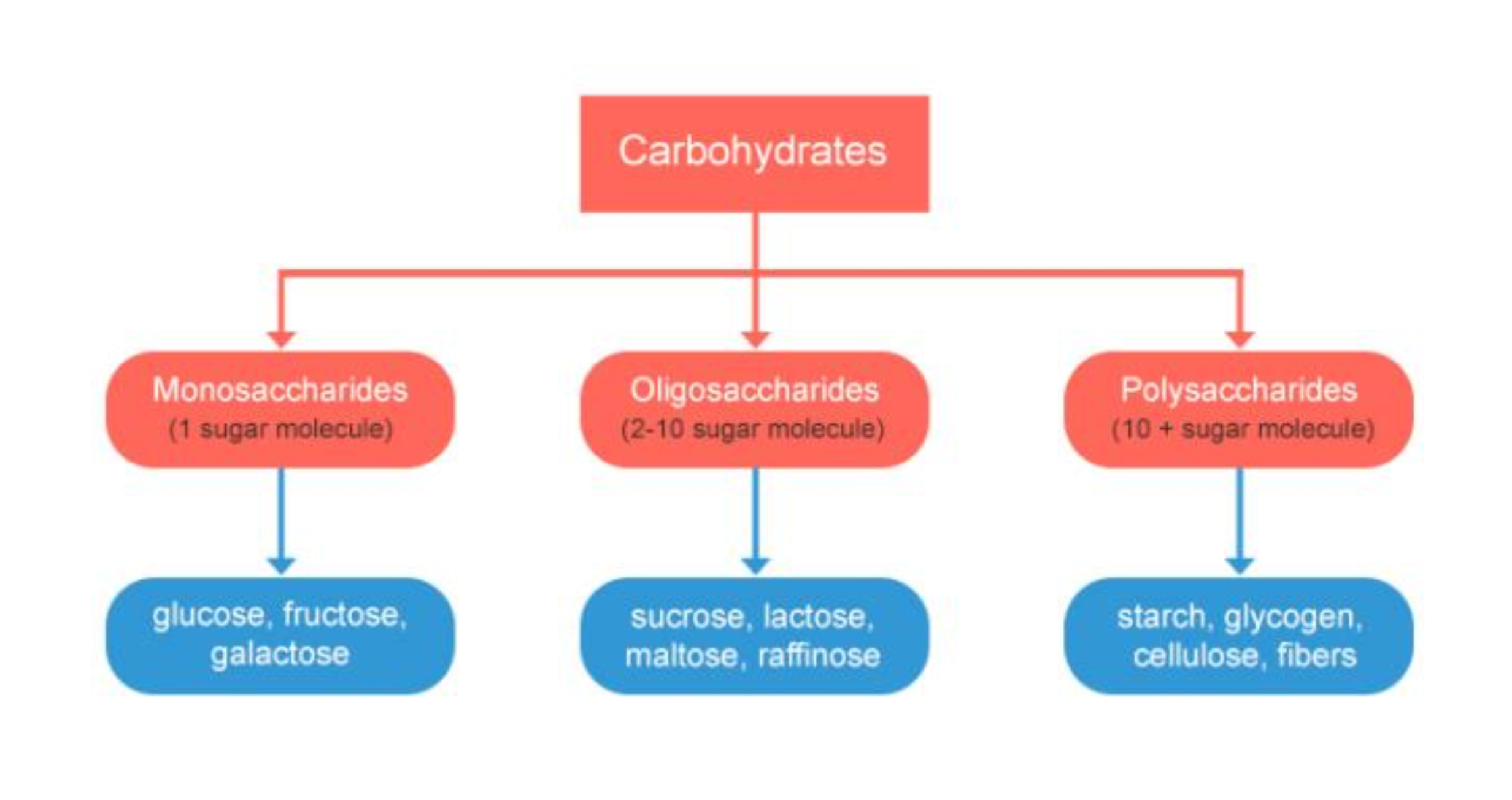
Types of Carbohydrates
Simple
- shorter time to break
- spikes in sugar level
Complex
- Takes longer to break down
Carbohydrates calculations
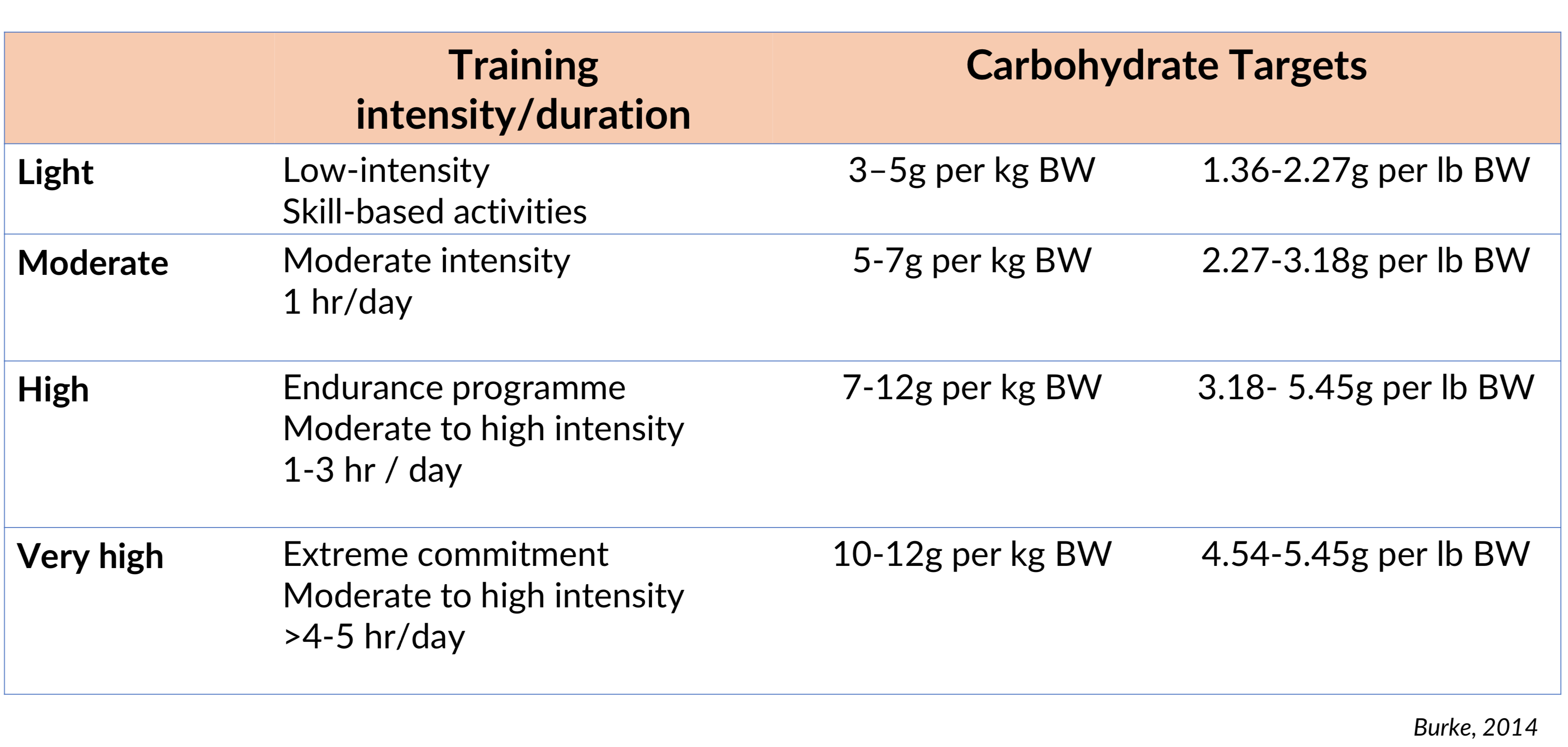
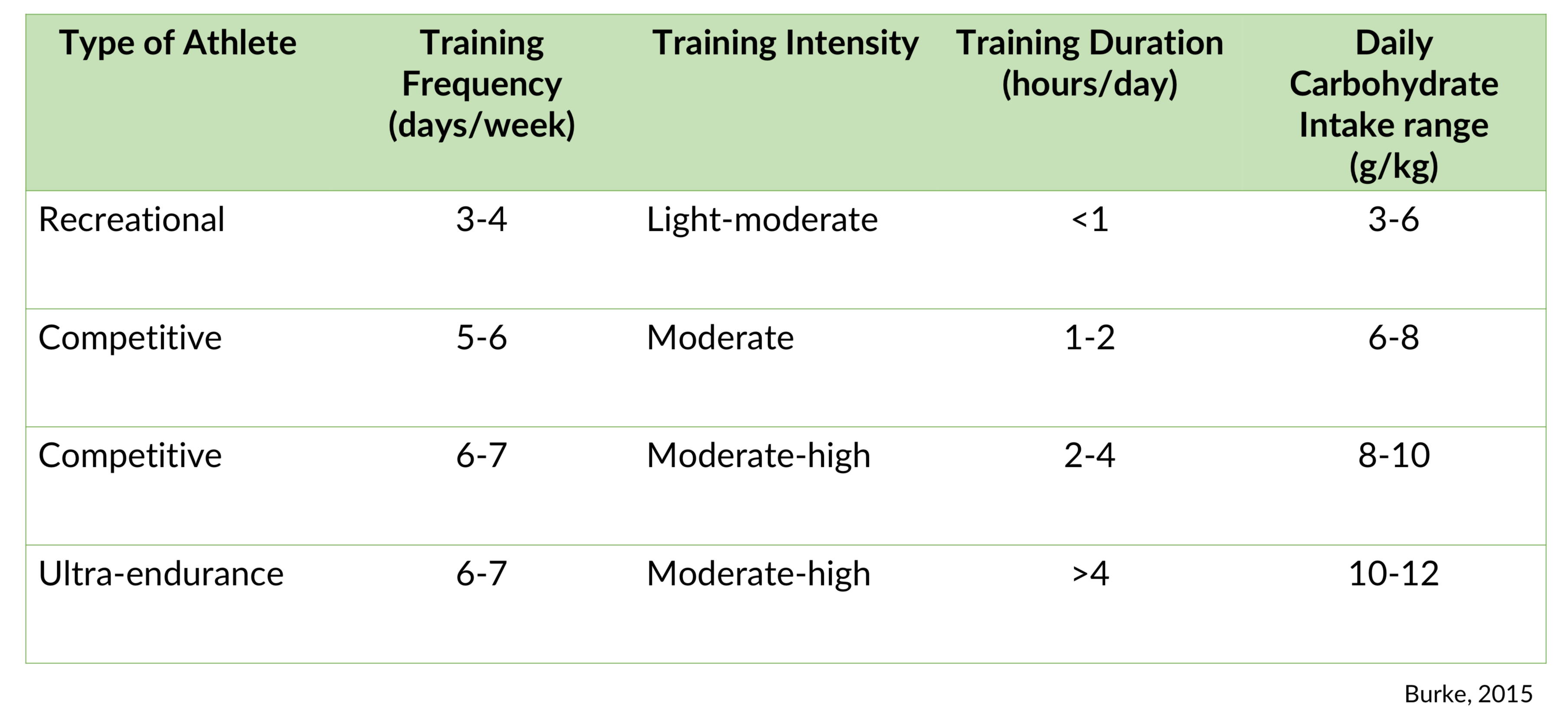
Sample carbohydrate calculation
- weight 75kg
- moderate exercise CHO 5-7 g/kg
CHO needs 75 * 5 = 375g to 75 * 7 = 525g
| Muscles | Glycogen stores grams/Kilogram |
|---|---|
| Trained | 32 |
| untrained | 13 |
- More training increases glycogen stores
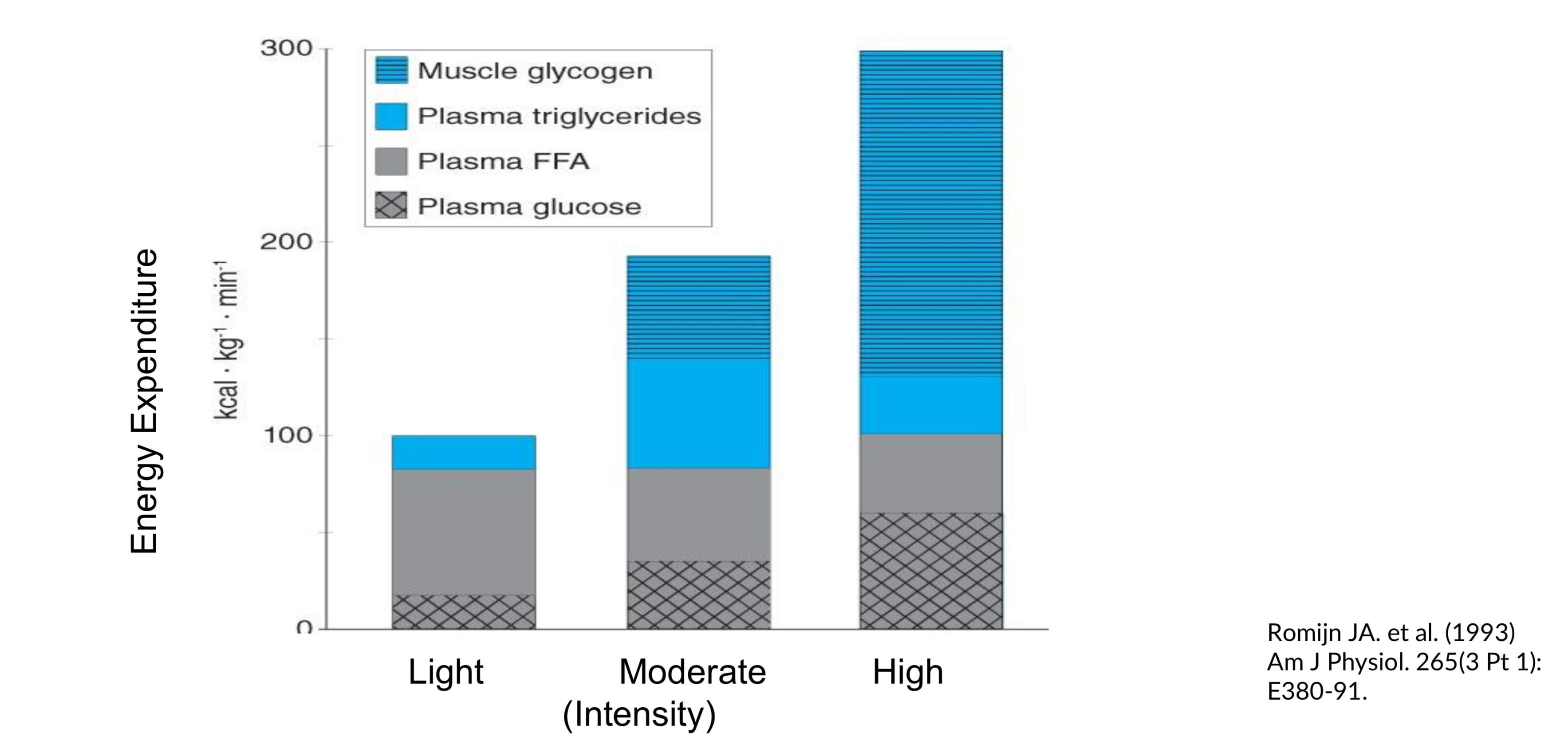
- Energy source at different exercise intensities
Energy Expenditure
Types of carbohydrates

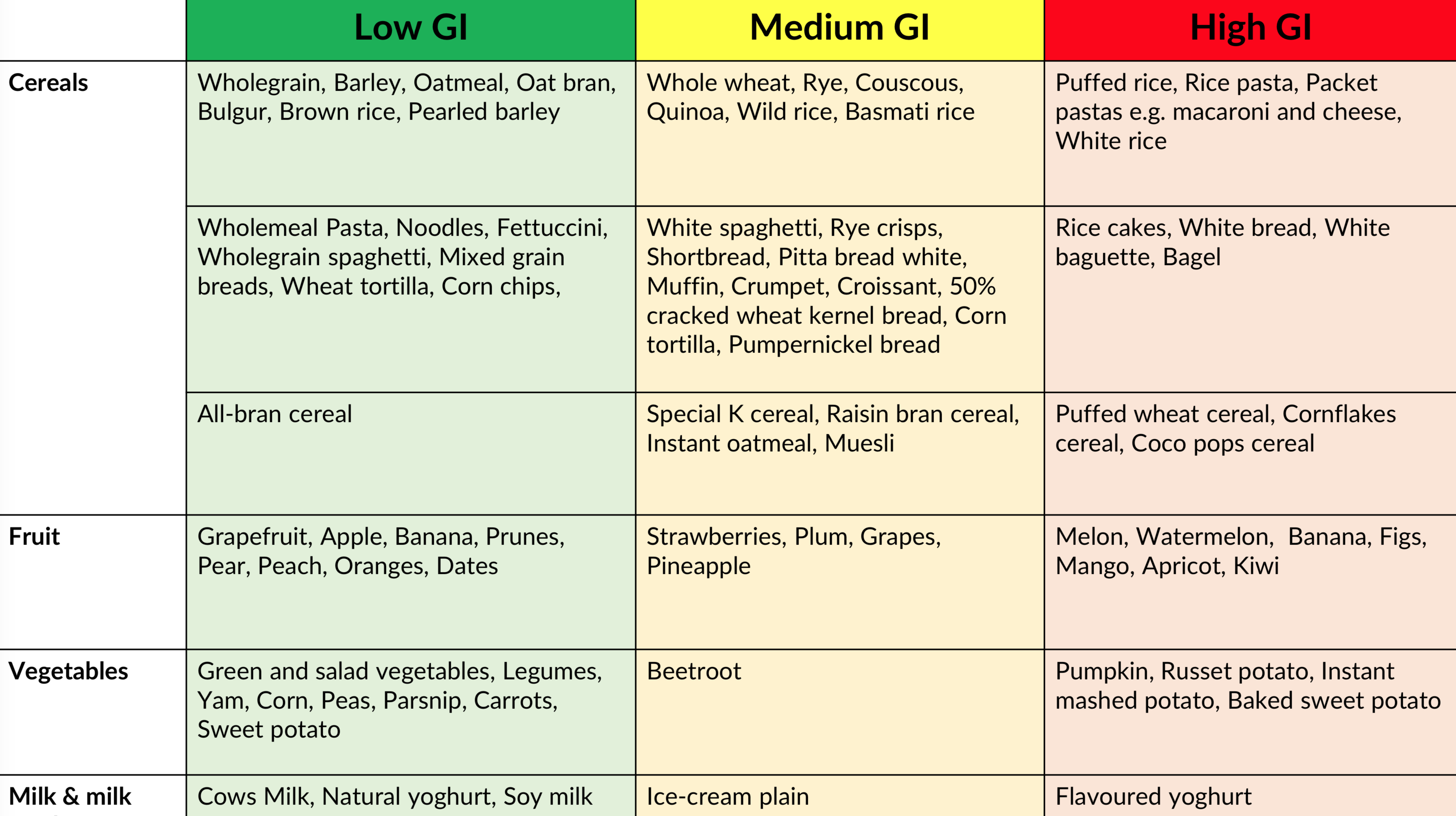
Glycaemic Index
Rate of absorbtion of Glycogen
-
Low Gi 0-54
-
Moderate GI 55-69
-
High GI 70+
Factors that influence Food GI
- Ripeness
- Storage time
- Processing
- Cooking Method
- Variety
- Protein content
Dietary Fibre
- Found in indgestible parts of the plants
- Keeps digestive system healthy
- Soluble fibre slows digestion of Carbohydrates - slow rise in blood glucose level
- Insoluble fibre prevents constipation
Insoluble Fibre
- Seeds wheat bran edible skins dried beans
- Passes through the body undigested
- Prevents constipation
Soluble Fibre
- Fruits vegetable flaxseed, oats, barley, beans
- Helps lower bad cholestrol
- Keeps you feeling fuller for longer