Professional Diploma in Sports Nutrition - Module 1 Lesson 1
Recently I started an online course on shawacademy.I signed up for the Professional Diploma in Sports Nutrition. The course is split into four modules and its taught by Amanda Broderick, who seemed to have a lot of knowledge in Sports Nutrition.
The first lession was titled “What Fuels Energy Systems”
My goal was to learn about Nutrition as I was sick of all the martketing gimmick around.
Nutrition comes from the word nourish which means to feed, nurse, support and preserve.
Week 1: Energy System and Carbohydrates
Week 2: Proteins, Fats, and Hydration.
Week 3: Supplements and Nutrient Timing
Week 4: Mastering Strategies for Wright Loss and Muscle Gain
Week 5: Mastering Energy Metabolism
Week 6: Mastering Fats
Week 7: Mastering CArbohydrates
Week 8: Mastering Proteins
Week 9: The Endurance athelete
Week 10: The Strength Athelete
Week 11: Team Sports
Week 12: Competition Preparation and Recovery
Week 13: Specialised Diets in Sports
Week 14: Mastering Suppements and Micronutrients
Week 15: Nutrition for injury and illness
Week 16: Delivering effective advice
Each individual needs are different and should to tailored to ones personal needs.
Areas of Sports Nutrition
- Energy Systems
- Competition nutrition
- Snacks
- Preparation
- Nutrients
- Carb loading
- Supplements
- Fluids
- Timings
- Recovery
- Weight Control
- Micronutrients
You cant out train a bad diet
Benefits of Good Sports Nutrition
- Refuels Energy stores
- Helps reach your weight loss/gain taargets
- Boosts immune system
- Improves performance
- Enhances concentration levels
- Delays fatigue
- Protects against injury
- Fights and helps to prevent disease
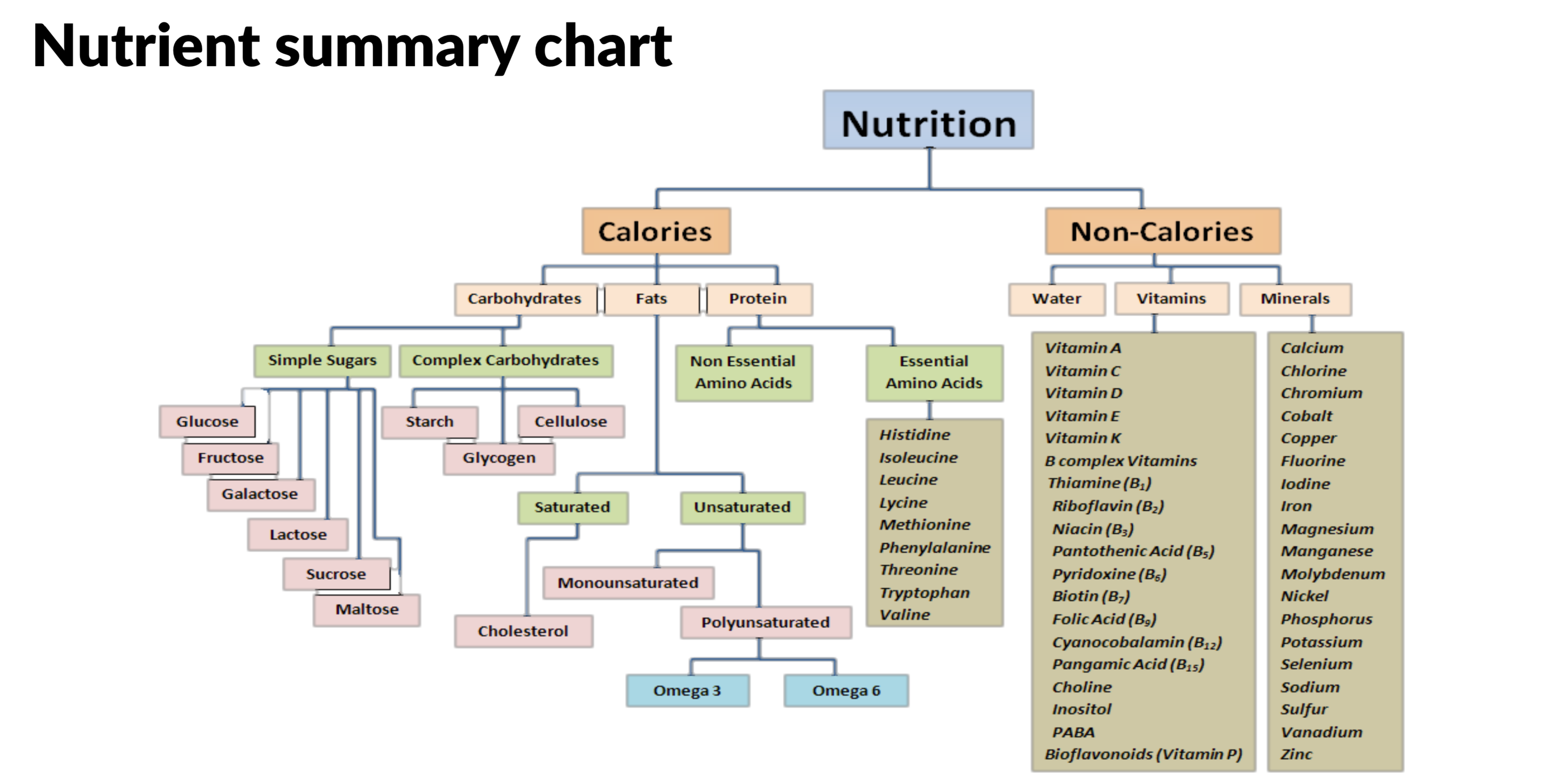
Carbohydrates
- Energy
- Principal source of energy
- Most important fuel for excercise
- Stored as glycogen in liver and muscles
- Maintain blood glucose levels
- Dietary energy 4 kcal/g (17KJ)
Fats
- Supply fuel for cells - 9 Kcals/g (38KJ)
- Energy dense
- Acts as a carrier for fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K) and antioxidants
- Insulate the body and provide energy
- Protective layer for organs
- Form brain tissues nerves cell membrane
Protein
- Growth and repair of tissues and cells
- Enzymatic function - all enxymes are protiens
- Hormonal function - eg insulin
- Buffering function - maintain pH balance of blood
- Energy 4kcal/g (17KJ)
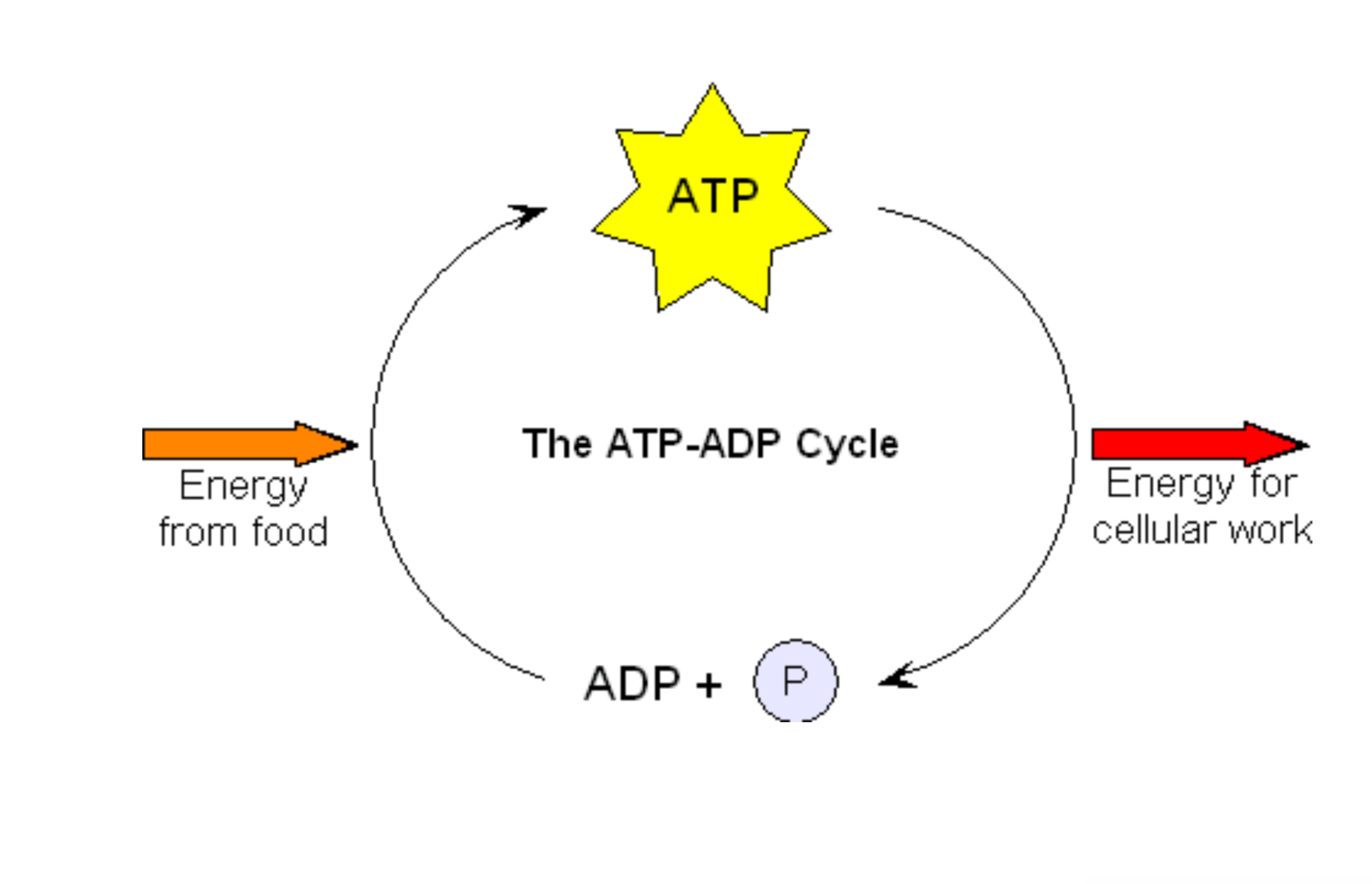
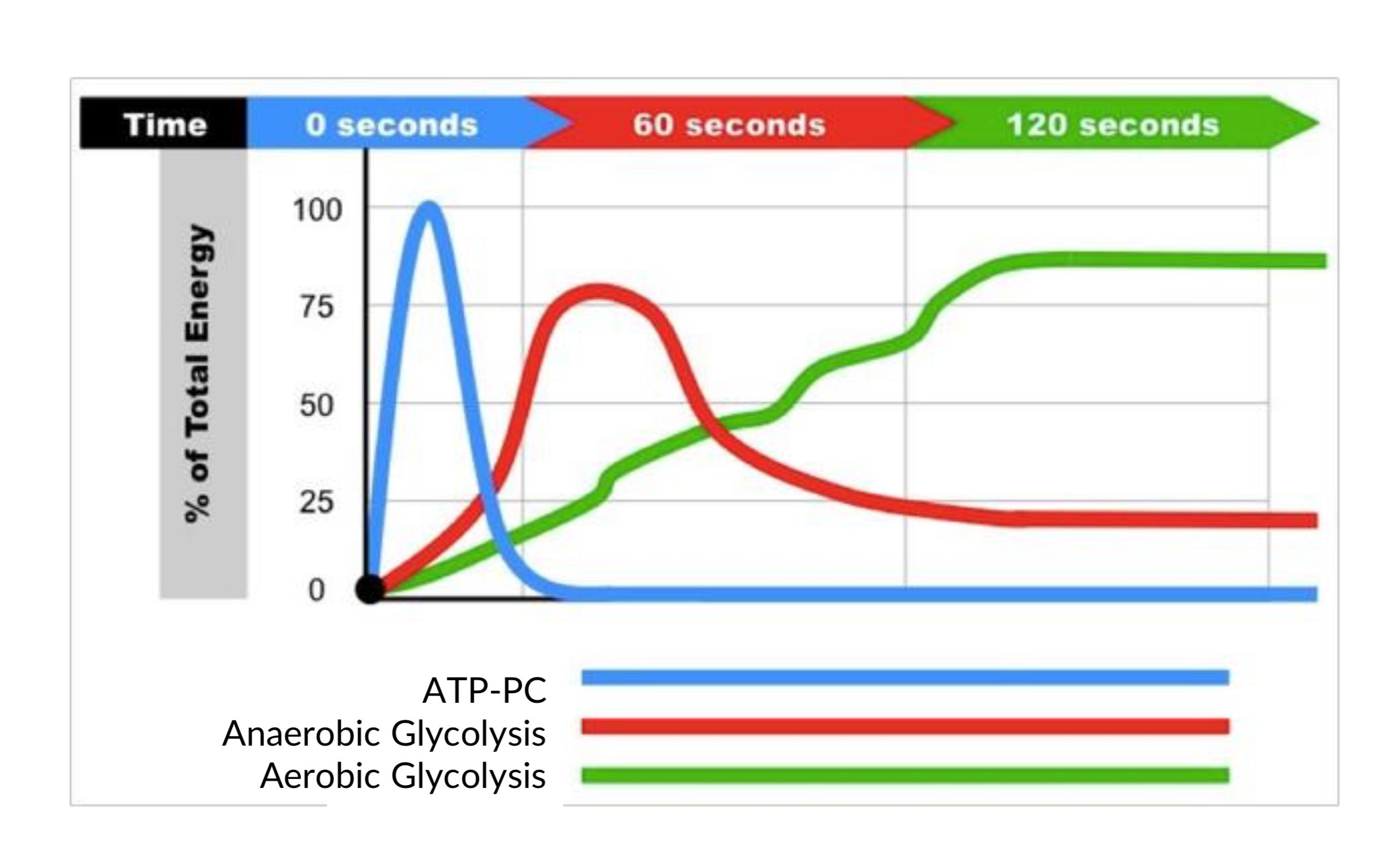
Energy systems
ATP - Adenosine Tri-Phosphate
Energy is produced by splitting phosphate group 3/4 energy is given off as heat
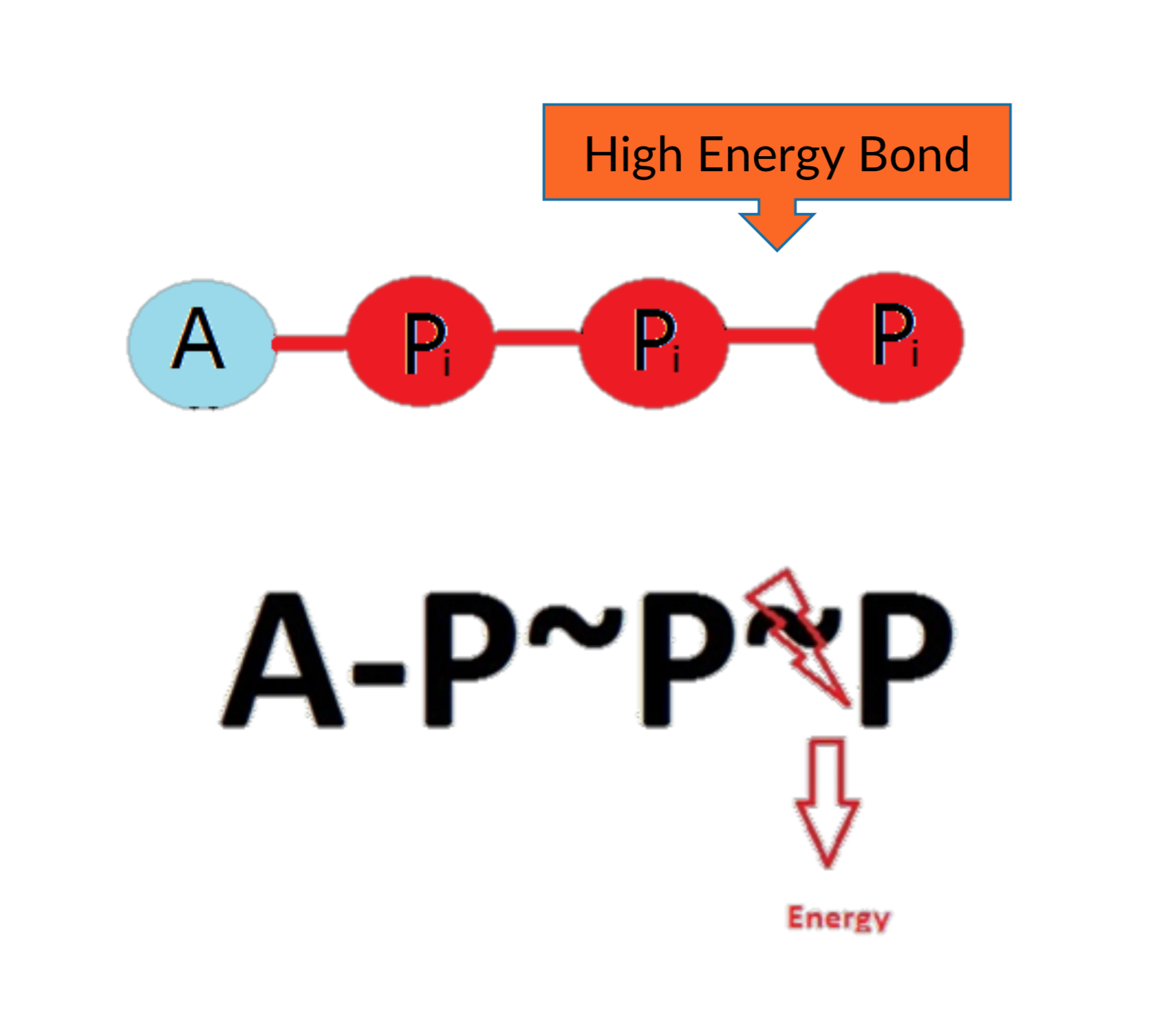
ATP-PC System
Provides energy for brief periods
- Short sprint
- Single jump
- Weight lift
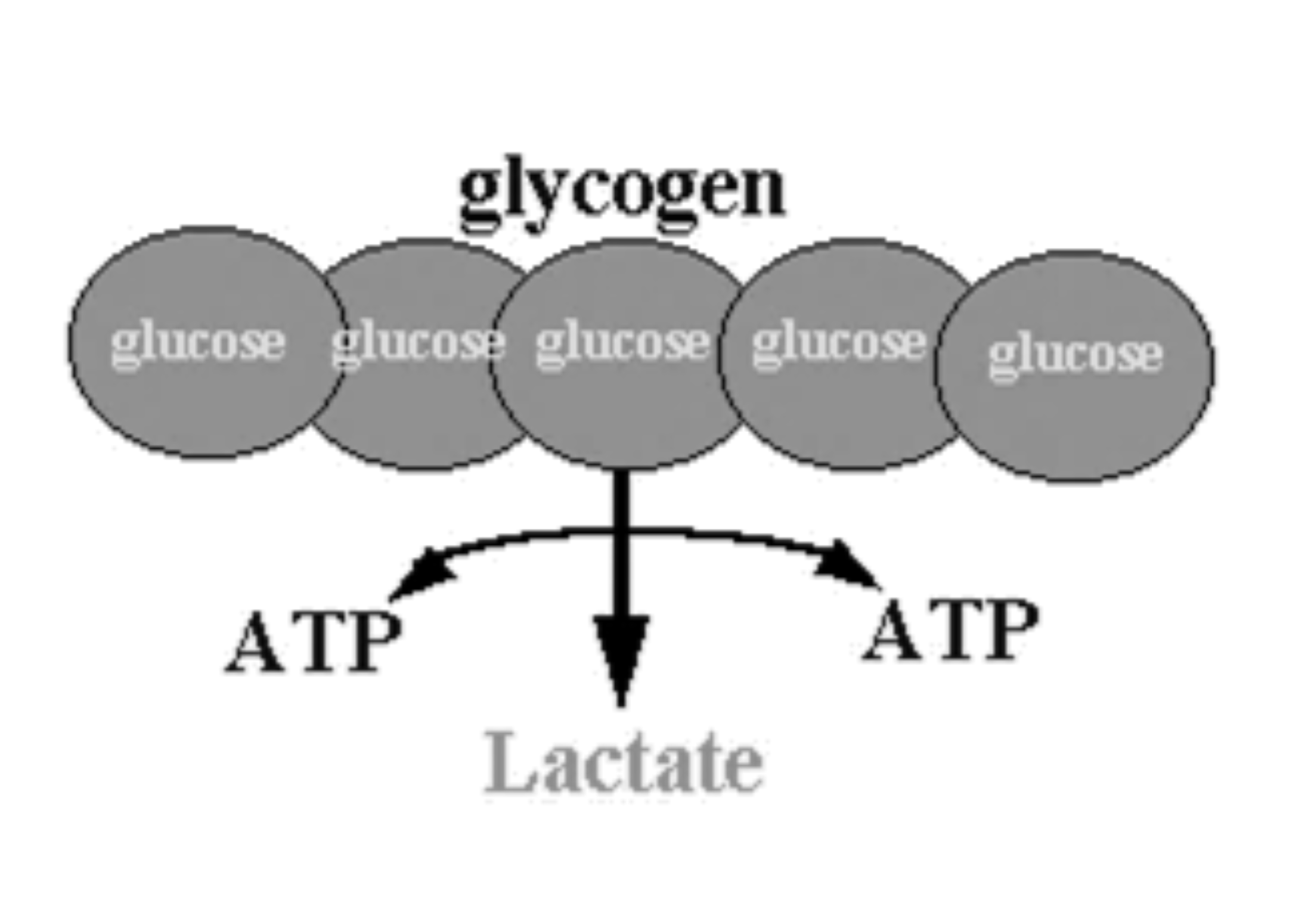
Anaerobic Glycolysis
- Activates in high intensity activity
- Lasts approximately 90 seconds
- Energy is produced by breaking down glucose
Aerobic Metabolism
- 20% more efficient than Anaerobic
- Uses carbohydreates and fats as ffule
- Produces large amounts of energy
Physical Fitness
Its the ability to carry out tasks without undue fatigue
Overall fitness is made up of five main components:
- Cardiorespiratory Endurance
- Endurance
- Strength
- Body composition
- Flexibility
Ideal Physical Acitivty : 18 - 64 years
- 150 minutes of moderate aerobic physical activity
- 300 for more benefit
- Muscle strengthening activities atleast twice a week.
| Level | Intensity |
|---|---|
| light | No noticeable change in breathing pattern |
| moderate | Breathing is deep and more frequent.You can carry on a conversation but not sing |
| high | Will break a sweat in 3-5 minutes.Rapid and deep breathing.You cna only talk in short phrases |